Ecological and phytochemical characterization of Galphimia spp. natural populations in the state of Aguascalientes
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29298/rmcf.v16i88.1479Keywords:
Galphimia, Aguascalientes, wild populationsAbstract
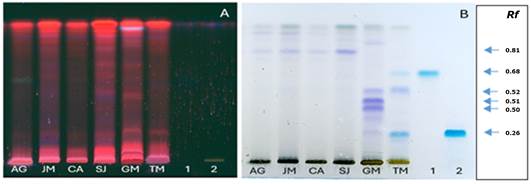
The Galphimia genus of the Malpighiaceae family contains 24 species, among the most representative are Galphimia gracilis, Galphimia angustifolia and Galphimia glauca. In México the latter distributes in the Central and Northeastern regions, where it exhibits anti-inflammatory, sedative, and anxiolytic properties. However, the presence and accumulation of bioactive metabolites such as galfimins, a type of triterpene, present in samples collected in the states of Guanajuato and Querétaro, and galphimins and galphimidins from the states of Guerrero and Morelos, have been reported in a few wild communities in Mexico. The objective of the present study was to generate ecological, morphological and phytochemical information associated with natural populations of Galphimia spp. in four sites at the state of Aguascalientes (Aguascalientes, Jesús María, Calvillo and San José de Gracia). Ecological conditions were assessed through an inventory for site recognition; morphological conditions with the methodology proposed by the International Plant Genetic Resources Institute and specialized taxonomic keys; and phytochemistry with plant samples from each population to determine the presence of triterpenes using automated thin layer and high-resolution liquid chromatographic techniques. The sites with the presence of Galphimia spp. in the state showed some degree of disturbance and environmental differences in soil and vegetation. Morphological and phenological characteristics did not detect differences between populations. The phytochemical profile did not show the presence of known galfimins and galphimidins in the populations. This is the first report on phytoecological and phytochemical analyses of natural populations of Galphimia spp. in Aguascalientes.
Downloads
References
Balderas, G. S., Alcalá, R. E., Ortíz-Caltempa, A., Cardoso-Taketa, A., & Villarreal, M. L. (2020). Variation in the production of sedative and anxiolytic compounds among Galphimia sp. populations grown in a greenhouse. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia, 30(1), 99-102. https://produccion.siia.unam.mx/Publicaciones/ProdCientif/PublicacionFrw.aspx?id=627207
Cardoso T., A. T., Lozada-Lechuga, J., Fragoso-Serrano, M., Villarreal, M. L., & Pereda-Miranda, R. (2004). Isolation of Nor-secofriedelanes from the sedative extracts of Galphimia glauca. Journal of Natural Products, 67(4), 644-649. https://doi.org/10.1021/np0304666
Cardoso-Taketa, A. T., Pereda-Miranda, R., Choi, Y. H., Verpoorte, R., & Villarreal, M. L. (2008). Metabolic profiling of the Mexican anxiolytic and sedative plant Galphimia glauca using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and multivariate data analysis. Planta Medica, 74(10), 1295-1301. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18612944/
Comisión Nacional Forestal. (2016). Manual para el establecimiento de unidades productoras de germoplasma forestal. Comisión Nacional Forestal. https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/docs/Manual_para_el_establecimiento_de_unidades_productoras_de_Germoplasma_Forestal.pdf
del Rayo C., M., Phillipson, J. D., Croft, S. L., Marley, D., Kirby, G. C., & Warhurst, D. C. (2002). Assessment of the antiprotozoal activity of Galphimia glauca and the isolation of new nor-secofriedelanes and nor-friedelanes. Journal of Natural Products, 65(10), 1457-1461. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12398543/
eFloraMEX. (2023, 1 de enero). Galphimia glauca Cav. eFloraMEX La flora electronica de México. https://efloramex.ib.unam.mx/cdm_dataportal/taxon/2dc66516-701a-4916-8657-0144b6048a4d
Espinosa O., D., Ocegueda C., S., Aguilar Z., C., Flores V., Ó., y Llorente-Bousquets, J. (2008). El conocimiento biogeográfico de las especies y su regionalización natural. En J. Soberón, G. Halffter y J. Llorente-Bousquets (Comps.). Capital natural de México Conocimiento actual de la biodiversidad (Vol. I, pp. 33-65). Comisión Nacional para el Conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/301839050_El_conocimiento_biogeografico_de_las_especies_y_su_regionalizacion_natural
Fournier, L. A. (1974). Un método cuantitativo para la medición de características fenológicas en árboles. Turrialba, 24, 422-423. https://www.scirp.org/reference/referencespapers?referenceid=1202016
Gesto-Borroto, R., Cardoso-Taketa, A., Yactayo-Chang, J. P., Medina-Jiménez, K., Hornung-Leoni, C., Lorence, A., & Villarreal, M. L. (2019). DNA barcoding and TLC as tools to properly identify natural populations of the Mexican medicinal species Galphimia glauca Cav. PLoS One, 14(5), Article e0217313. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0217313
González-Cortazar, M., Herrera-Ruiz, M., Zamilpa, A., Jiménez-Ferrer, E., Marquina, S., Alvarez, L., & Tortoriello, J. (2014). Anti-inflammatory activity and chemical profile of Galphimia glauca. Planta Medica, 80(1), 90-96. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24338551/
Instituto Nacional de Estadísticas y Geografía (Inegi). (2022). Mapas. Biblioteca digital de Mapas. Conjunto de datos vectoriales. https://www.inegi.org.mx/app/mapas/
International Board for Plant Genetic Resources Institute. (1980). Tropical fruit descriptors. International Board for Plant Genetic Resources. https://cgspace.cgiar.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/89e7bce2-b5d2-4126-8a51-aa683ce179cb/content
León-Álvarez, E., Millán P., C., Gesto-Borroto, R., Acosta-Urdapilleta, M. de L., Téllez-Téllez, M., Barreto G., R., Núñez-Aragón, P. N., Villareal, M. L., & Cardoso T., A. T. (2024). Anti-inflammatory, radical-scavenging, and chelating activities of Nor-Triterpenes from Galphimia species. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia, 34(3), 553-563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-023-00506-3
Lot, A., y Chiang, F. (1986). Manual de herbario. Administración y manejo de colecciones, técnicas de recolección y preparación de ejemplares botánicos. Consejo Nacional de la Flora de México, A. C. https://issuu.com/jpintoz/docs/1986_lot-chiang_manualherbario_cnfm
McRoberts, R. E., Tomppo, E. O., y Czaplewski, R. L. (1992). Diseños de muestreo de las Evaluaciones Forestales Nacionales. En Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Alimentación y la Agricultura (ONUAA). Antología de conocimiento para la evaluación de los recursos forestales nacionales (pp. 1-21). ONUAA. https://www.fao.org/fileadmin/user_upload/national_forest_assessment/images/PDFs/Spanish/KR2_ES__4_.pdf
NOM-021-RECNAT-2000. (2001, 14 de agosto). Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-021-RECNAT-2000, Que establece las especificaciones de fertilidad, salinidad y clasificación de suelos. Estudios, Muestreo y Análisis. Diario Oficial de la Federación, Segunda Sección, de 31 de diciembre de 2002. https://www.ordenjuridico.gob.mx/Documentos/Federal/wo69255.pdf
NOM-059-SEMARNAT-2010. (2010, 26 de noviembre). Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-059-SEMARNAT-2010, Protección ambiental-Especies nativas de México de flora y fauna silvestres-Categorías de riesgo y especificaciones para su inclusión, exclusión o cambio-Lista de especies en riesgo. Diario Oficial de la Federación, Segunda Sección, de 30 de diciembre de 2010. https://biblioteca.semarnat.gob.mx/janium/Documentos/Ciga/agenda/DOFsr/DO2454.pdf
Rios, M. Y., Ortega, A., Domínguez, B., Déciga, M., & de la Rosa, V. (2020). Glaucacetalin E and galphimidin B from Galphimia glauca and their anxiolytic activity. Journal of Etnopharmacology, 259, 112939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2020.112939
Romahn de la V., C. F., y Ramírez M., H. (2010). Dendrometría. División de Ciencias Forestales de la Universidad Autónoma de Chapingo. https://dicifo.chapingo.mx/pdf/publicaciones/dendrometria.pdf
Rzedowski, J. (2006). Vegetación de México. Comisión Nacional para el Conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad. https://www.biodiversidad.gob.mx/publicaciones/librosDig/pdf/VegetacionMxPort.pdf
Sharma, A., Folch, J. L., Cardoso-Taketa, A., Lorence, A., & Villarreal, M. L. (2012a). DNA barcoding of the Mexican sedative and anxiolytic plant Galphimia glauca. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 144(2), 371-378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2012.09.022
Sharma, A., Cardoso-Taketa, A., Choi, Y. H., Verpoorte, R., & Villarreal, M. L. (2012b). A comparison on the metabolic profiling of the Mexican anxiolytic and sedative plant Galphimia glauca four years later. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 141(3), 964-974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2012.03.033
Siqueiros D., M. E., Rodríguez Á., J. A., Martínez R., J., Sierra M., J. C., y García R., G. (2017). Vegetación del Estado de Aguascalientes (1ra Edición). Comisión Nacional para el Conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad y Universidad Autónoma de Aguascalientes. https://editorial.uaa.mx/docs/ve_vegetacion_aguascalientes.pdf
Siqueiros D., M. E. (2024, 11 de mayo). Inventario florístico de familias selectas de dicotiledóneas del estado de Aguascalientes. Version 1.11. Comisión Nacional para el Conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad. https://www.gbif.org/es/dataset/d056f586-b5a0-494c-990b-854ddfe18f77
Stevens, P. F. (2024, April 10). Angiosperm PhylogenyWebsite. Version 14. Missouri Botanical Garden. http://www.mobot.org/MOBOT/research/APweb/
Tortoriello, J., & Lozoya, X. (1992). Effect of Galphimia glauca methanolic extract on neuropharmacological tests. Planta Medica, 58(3), 234-236. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-961442
Villaseñor, J. L. (2016). Checklist of the native vascular plants of Mexico. Revista Mexicana de Biodiversidad, 87, 559-902. https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/425/42547314001.pdf
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Forestales

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
The authors who publish in Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Forestales accept the following conditions:
In accordance with copyright laws, Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Forestales recognizes and respects the authors’ moral right and ownership of property rights which will be transferred to the journal for dissemination in open access.
All the texts published by Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Forestales –with no exception– are distributed under a Creative Commons License Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0), which allows third parties to use the publication as long as the work’s authorship and its first publication in this journal are mentioned
The author(s) can enter into independent and additional contractual agreements for the nonexclusive distribution of the version of the article published in Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Forestales (for example, include it into an institutional repository or publish it in a book) as long as it is clearly and explicitly indicated that the work was published for the first time in Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Forestales.
For all the above, the authors shall send the form of Letter-transfer of Property Rights for the first publication duly filled in and signed by the author(s). This form must be sent as a PDF file to: ciencia.forestal2@inifap.gob.mx
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 4.0 International license.





